Can Bread Go in Compost? A Comprehensive Guide to Composting Bread Safely

Composting is an eco-friendly way to recycle organic waste, but not all food items are suitable for this process. One common question among compost enthusiasts is whether bread can safely be added to compost piles. While bread is biodegradable, there are important factors to consider to avoid attracting pests and maintaining a balanced compost environment. This comprehensive guide will explore the feasibility of composting bread, the potential benefits and drawbacks, and best practices for incorporating it into your composting routine. Understanding these elements will help you make informed decisions and enhance the effectiveness of your composting efforts.
Can Bread Be Added to Compost?
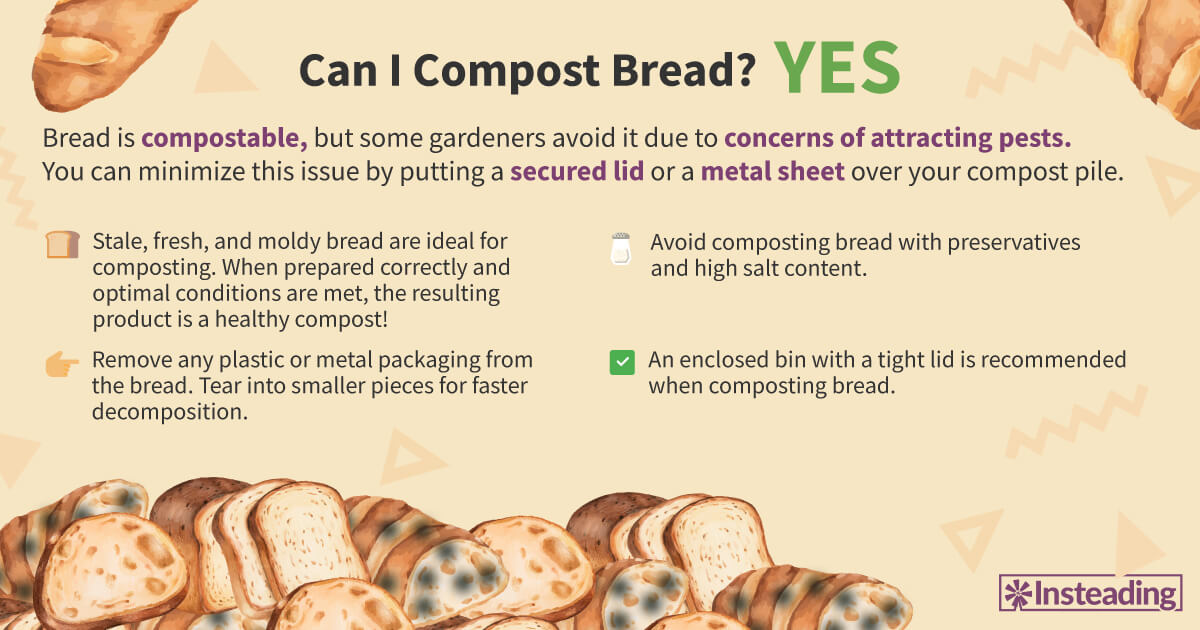
Yes, bread can be added to compost, but it's important to do so in moderation. When included in compost, bread provides valuable organic matter that can enhance the microbial activity in the compost pile. However, due to its high carbohydrate content, it can attract unwanted pests like rats and other critters if used excessively. To mitigate this risk, it is advisable to bury the bread deep within the compost, mixing it well with other greens and browns to maintain a balanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. Additionally, using stale or moldy bread is preferable, as it hastens the decomposition process compared to fresh bread.
Benefits of Composting Bread
Composting bread contributes several benefits, including adding nutrients to the soil. Bread breaks down into carbon, which helps in building rich organic matter in compost. Moreover, it encourages microbial life, leading to a more balanced and effective compost pile. By composting bread, you are recycling food waste, which reduces landfill contributions and promotes sustainable practices.
Potential Issues with Composting Bread
While composting bread has advantages, it can lead to potential issues as well. One of the main concerns is the attraction of pests and rodents. Bread's high starch content is a food source for many unwanted animals, and if not managed properly, it can disrupt the composting process. Another issue is the probability of bread mold developing, which might lead to an imbalance in the compost’s pH level if excessive amounts are added.
Best Practices for Composting Bread
To compost bread safely, it's essential to follow a few best practices. First, always chop or tear the bread into smaller pieces to speed up the decomposition process. Second, mix bread with a variety of other compost materials, such as kitchen scraps and yard waste, to maintain a proper carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. Lastly, avoid adding any oily or heavily processed breads, as these can lead to foul odors and attract pests.
Types of Bread Suitable for Composting
Most types of bread can be composted, including white, whole wheat, and even gluten-free varieties. However, bread that contains large amounts of preservatives or artificial ingredients should be composted with caution. Stale bread is preferable, as it tends to break down faster in the compost. Additionally, bread products like rolls or bagels can also be composted, provided they are cut into smaller pieces.
How to Avoid Complications When Composting Bread
To minimize complications from composting bread, it is crucial to maintain a balanced compost. This involves ensuring that for every portion of bread added, an equal amount of other compostable materials, like fruits and vegetables, is included. Keeping your compost pile aerated by regularly turning it will help avoid bad odors and deter pests. It's also advisable to monitor moisture levels, as bread can retain a lot of water, leading to potential issues with saturation.
| Type of Bread | Suitability for Composting |
|---|---|
| White Bread | Yes |
| Whole Wheat Bread | Yes |
| Gluten-Free Bread | Yes |
| Bread with Preservatives | Caution |
| Stale Bread | Preferred |
Is bread allowed in compost?
Composting is a fantastic way to reduce waste and create nutrient-rich soil for gardening or landscaping. However, not all food items are suitable for composting. Bread can be a controversial addition to compost piles. Generally, bread is allowed in compost, but there are important considerations to keep in mind to ensure successful decomposition and prevent attracting pests.
Benefits of Composting Bread
Composting bread offers several benefits that can enhance the nutrient content of your compost pile:
- Nutrient-Rich Carbon Source: Bread contributes a significant amount of carbon, which is essential for the composting process.
- Reduces Food Waste: Composting unused or stale bread helps divert food waste from landfills, promoting a more sustainable environment.
- Improves Soil Structure: As bread decomposes, it creates a more loamy texture in the compost, which can benefit your garden soil.
Potential Issues with Composting Bread
While bread can be composted, it is vital to consider potential issues that may arise:
- Pest Attraction: Bread can attract pests such as rats and other rodents if not properly managed.
- Mold Growth: Decomposing bread may lead to mold, which can be an issue if you are concerned about plant health.
- Imbalance in Compost Ratio: Adding too much bread can create an unbalanced carbon-to-nitrogen ratio, hindering the composting process.
Best Practices for Composting Bread
To effectively compost bread, follow these best practices to ensure a successful composting process:
- Limit Quantity: Use bread as a supplement rather than the main ingredient in your compost pile.
- Chop or Tear: Breaking bread into smaller pieces can accelerate the decomposition process and reduce the chance of clumping.
- Add Greens: Balance the bread with a good amount of green materials such as fruit scraps or vegetable peelings to maintain a healthy carbon-nitrogen ratio.
Alternative Options for Old Bread
If you're hesitant to add bread to your compost pile, consider these alternative options for using old bread:
See also:
- Bread Pudding: Transform stale bread into a delicious bread pudding for a creative cooking option.
- Bird Feed: Crumbled bread can be a great winter food source for birds and other wildlife in your area.
- Homemade Croutons: Repurpose stale bread into croutons for salads or soups, reducing waste while creating a tasty snack.
Deciding Factors for Composting Bread
When deciding whether to compost bread, consider these deciding factors:
- Type of Bread: Whether the bread is white, whole grain, or contains nuts and seeds can impact how it decomposes and affects the compost pile.
- Condition: Fresh bread, moldy bread, or bread with additives (like oils or preservatives) should be treated differently to maintain compost health.
- Your Composting System: Evaluate whether your composting method can handle bread without attracting pests or causing imbalances.
Why can't I compost bread?

Bread is often considered unsuitable for composting for several reasons that can negatively impact compost quality and attract pests. Here are some key points to understand this issue better.
Microbial Imbalance
When you add bread to a compost pile, it can upset the microbial balance. Bread is largely made up of carbohydrates, which can lead to a rapid growth of specific fungal species. This can create an imbalance that favors certain microorganisms over others, potentially leading to poor decomposition and a slower composting process. An imbalance can manifest in several ways:
- The proliferation of fungi over beneficial bacteria.
- A decrease in overall compost temperatures, which are necessary for pathogen and weed seed destruction.
- An increase in stagnant conditions that could lead to unpleasant odors.
Pest Attraction
Another major issue with composting bread is its ability to attract a variety of pests, such as rodents and other animals. Bread serves as a food source for these creatures, potentially leading to infestations in your compost pile. Managing pest issues can be particularly challenging, and this can lead to a few concerns:
- Rodents digging through the compost, creating a mess.
- Unexpected visits from raccoons or birds looking for an easy meal.
- The spread of pests from the compost to surrounding areas, creating a nuisance.
High Gluten Content
Bread contains high levels of gluten, which can become a hindrance in composting. Gluten can form a sticky mass in wet conditions, which makes it difficult for oxygen to penetrate and slows down the decomposition process. This results in:
- Compacted layers within the compost pile that hinder aerobic decomposition.
- Increased likelihood of anaerobic conditions, leading to foul smells.
- Production of a dense, clumpy mixture that is less aerated.
Potential for Mold Growth
Due to its high moisture and carbohydrate content, bread is susceptible to mold growth during composting. Mold can be an issue for several reasons:
- It can outcompete beneficial microbes, leading to inefficient composting.
- Some molds can be harmful to humans and pets, posing health risks.
- Mold can create an unwanted aesthetic and odor issues in your compost pile.
Compounding Food Waste Problems
Composting bread may not be the most efficient way to manage food waste. Instead of providing benefits to the composting system, it can cause a compounding of existing issues. The negative effects of adding bread can include:
- Slower breakdown and an increase in waste volume.
- Increased complexity in managing compost quality and materials.
- The possibility of released methane gas from anaerobic decomposition if not properly aerated.
Can I put bread into my compost bin?

Yes, you can put bread into your compost bin, but there are important factors to consider. Bread is categorized as a green material in composting, which means it has a higher nitrogen content. However, its inclusion can lead to several potential issues if not managed properly. Here are some details to help you understand the nuances of composting bread effectively.
Benefits of Composting Bread
Composting bread can contribute to a well-balanced compost mixture, adding valuable nutrients. The advantages include:
- Nitrogen Source: Bread, being a protein-rich food, adds nitrogen to the compost.
- Beneficial Microorganisms: The decomposition of bread supports the growth of microorganisms that enhance soil health.
- Moisture Retention: Bread can help maintain moisture levels in your compost bin, aiding the overall decomposition process.
Potential Issues with Bread in Compost
While bread has benefits, it can also introduce complications. These issues involve:
- Attracting Pests: Bread is highly appealing to rodents and insects, which may become a nuisance.
- Mold Growth: Excessive bread can promote mold, which, while harmless in small amounts, can be problematic in larger quantities.
- Odor Problems: Decomposing bread might emit unpleasant odors if not balanced with other materials.
How to Compost Bread Effectively
To mitigate potential problems when composting bread, follow these tips:
See also:
- Moderation: Limit the amount of bread you add; it should not exceed 10% of your total compost volume.
- Mix with Greens: Combine bread with high-carbon materials like dried leaves or straw to balance nitrogen levels.
- Bury Deep: Place bread in the center of the compost to minimize exposure and reduce pest attraction.
Types of Bread Suitable for Composting
Not all bread is made equal when it comes to composting. Suitable types include:
- Stale Bread: Old bread that is no longer fit for consumption breaks down easily.
- Whole Grain: Whole grain bread provides more nutrients and beneficial microbes for the compost.
- Crusts and End Pieces: Parts of the bread that are often thrown away can be composted to reduce waste.
Alternatives to Composting Bread
If you're hesitant about composting bread, consider these alternatives:
- Feeding Animals: Check if local farm animals can safely consume stale bread.
- Food Rescue Programs: Donate usable bread to local shelters or food banks.
- Dehydration: Drying bread to make breadcrumbs can extend its life and reduce waste.
Why can't you put bread in compost?

Bread is commonly considered unsuitable for composting for several reasons. Although it is an organic matter, there are specific concerns that make it less than ideal for compost piles. Here are some of the primary reasons why bread should be avoided in compost:
Potential for Mold Growth
Adding bread to your compost can promote the growth of mold. This is because bread is rich in carbohydrates and can provide an ideal environment for various molds to thrive. These molds can:
- Compete with beneficial microorganisms essential for decomposition.
- Lead to an unpleasant odor, indicating improper composting.
- Potentially introduce harmful pathogens into the compost mix.
Attraction of Pests
Bread is known to attract various pests, including rodents and insects. The presence of these pests can disrupt the composting process and create more significant hygiene issues, such as:
- Exposure of compost to unwanted visitors, which often leads to further food waste problems.
- Increased competition for space and resources among the composting organisms.
- The possibility of pests carrying pathogens that may affect plants.
Imbalance in Nutrient Ratios
Composting requires a careful balance of carbon and nitrogen materials, often referred to as the C:N ratio. Bread predominantly contributes to the carbon side of the equation without providing enough nitrogen. This imbalance can lead to:
- Slower decomposition rates as microorganisms struggle to break down carbon-heavy materials.
- Increased likelihood of anaerobic conditions, leading to foul odors and a less effective composting process.
- Difficulty in achieving a balanced mixture, compromising the overall health of the compost pile.
Possible Presence of Additives
Many types of bread contain additives and preservatives that may not break down easily in compost. These can include:
- Artificial colors or flavors that may disrupt microbial activity.
- Preservatives like calcium propionate, which can inhibit the growth of beneficial microorganisms.
- Potential toxins that could leach into the soil and affect plant health.
Risk of Compaction
When bread is added to compost, it can become compact and form a dense layer that inhibits airflow. Proper aeration is crucial for aerobic composting. A lack of airflow can result in:
- Increased risk of anaerobic decomposition, leading to the production of methane and bad odors.
- Difficulty for microorganisms to thrive and facilitate the breakdown of material.
- Longer composting times, which delays the readiness of finished compost for garden use.
Questions from Our Readers
Can bread be composted?
Yes, bread can be composted, but it should be done in moderation. Bread is a carbon-rich material, which is beneficial for composting; however, if added in large quantities, it can attract pests and create smell issues.
How should I prepare bread before composting?
Before adding bread to your compost, it's best to tear it into smaller pieces to help it decompose faster. You can also mix it with greens like vegetables to maintain a proper carbon-to-nitrogen ratio in the compost pile.
What types of bread can I compost?
You can compost various types of bread, including white, whole grain, and stale bread. However, avoid composting bread with highly perishable toppings, such as butter or cheese, as these can attract unwanted animals to your compost pile.
Are there any risks associated with composting bread?
Yes, one risk of composting bread is that it may mold if not properly managed, which can lead to unpleasant odors and potential pest problems. To minimize this, ensure you balance bread with other compost materials and maintain good aeration.
See also:
If you want to read more articles like Can Bread Go in Compost? A Comprehensive Guide to Composting Bread Safely, we recommend you check out our Compost category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles