Discovering What is the Oldest Fruit to Exist? A Journey Through Time

The quest to identify the oldest fruit on Earth is a captivating journey that intertwines botany, history, and culture. As we delve into the annals of time, we uncover the rich evolutionary story of fruits that have thrived for millennia. These ancient varieties not only hold secrets to our agricultural past but also offer insights into the resilience and adaptability of nature. From prehistoric landscapes to modern orchards, this exploration invites us to appreciate the fruits that have nourished humanity across generations. Join us as we peel back the layers of history to discover what truly is the oldest fruit to exist.
What is the Oldest Fruit to Exist?
The title of the oldest fruit is often attributed to the fig (Ficus carica), which has been cultivated for thousands of years and holds a special place in agricultural history. Evidence of fig cultivation dates back to around 5,000 BC in the regions of the Middle East, particularly in places like Jericho. This remarkable fruit is not only favored for its sweet taste and nutritional benefits, but it also features prominently in various cultures and religions, symbolizing fertility and prosperity. The fig tree is known for its remarkable adaptability and resilience, allowing it to thrive in various climates, and its rich history makes it not only one of the oldest cultivated fruits but also a significant contributor to the development of agriculture.
Historical Significance of Figs
Figs have been an essential part of human civilization since ancient times, referenced in historical texts and various religious scriptures. They were a significant source of nutrition for early agrarian societies, often providing sustenance during periods of scarcity. In ancient Egypt, figs were revered and used in burial practices, symbolizing life after death. Furthermore, fig trees were cultivated in the ancient Mediterranean landscapes, representing the relationship between humans and the natural environment.
Botanical Classification
Figs belong to the genus Ficus within the Moraceae family, which includes over 750 species of flowering plants. The common fig, characterized by its unique peanut-shaped fruits, is specifically known as Ficus carica. The tree grows up to 10 meters tall and thrives in warm, temperate climates. Its fruits develop from a special structure known as a syconium, making the fig fruit a unique botanical entity. Understanding its botanical classification is crucial for appreciating its diversity and significance in various ecosystems.
Figs in Culinary Use
Figs have consistently played a crucial role in various cuisines around the world, appreciated for their sweetness and rich flavor. They can be consumed fresh, dried, or used in an array of dishes from appetizers to desserts. The unique texture of figs adds depth to salads, while their natural sugars make them an excellent choice for baked goods. In Mediterranean cuisine, they are often paired with cheeses and nuts, creating a delightful balance of flavors and textures that enhances culinary experiences.
Nutritional Benefits of Figs
Figs are not only delicious but also packed with nutritional benefits. They are an excellent source of fiber, essential for digestive health, and are rich in vitamins such as A, B, and K. Additionally, they provide minerals like potassium, magnesium, and calcium, which are vital for maintaining bone health and muscular function. The concentration of antioxidants found in figs also contributes to reducing inflammation and promoting overall health, making them a valuable addition to any diet.
Modern Cultivation and Variants
Today, figs continue to be cultivated globally, with significant production in countries such as Turkey, Iran, and the United States. The cultivation practices have evolved, integrating modern agricultural techniques to enhance yield and sustainability. Modern cultivars have been developed to improve disease resistance and adaptability to various growing conditions. This ongoing commitment to fig cultivation not only preserves the ancient varieties but also promotes new flavors and textures that cater to current consumer preferences.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Ficus carica |
| Origin | Middle East |
| Historical Cultivation Date | 5000 BC |
| Nutritional Content | High in fiber, vitamins, and minerals |
| Culinary Uses | Fresh, dried, salads, desserts |
Is a fruit or vegetable?
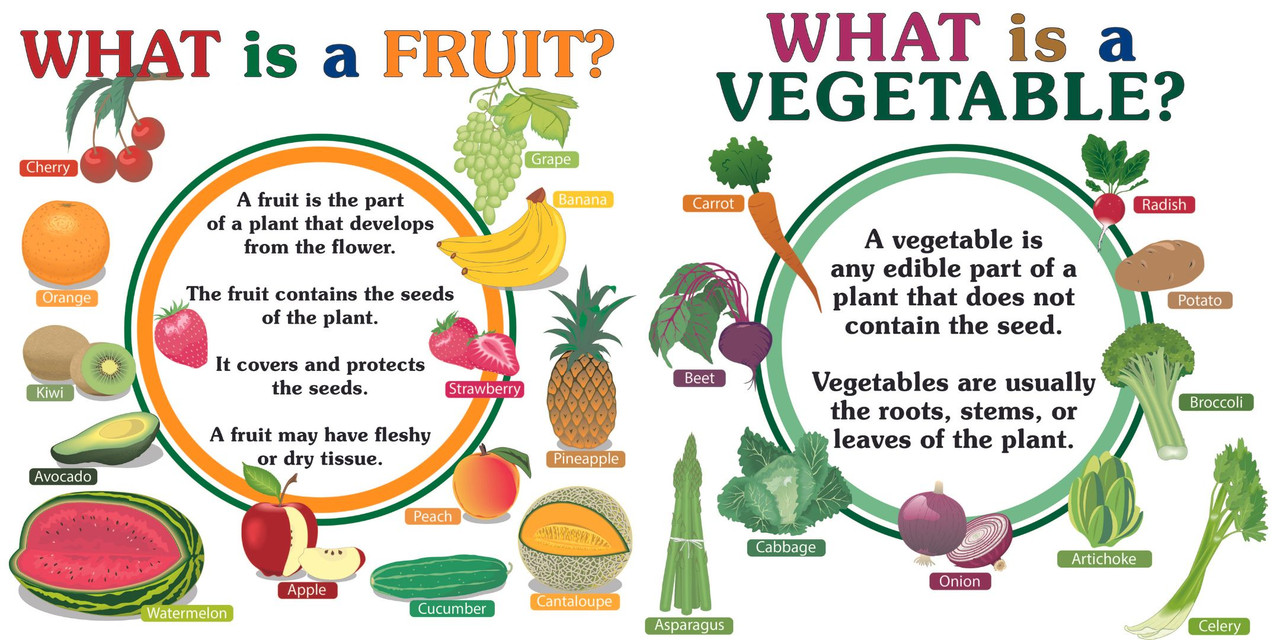
Eggplant, also known as aubergine, is botanically classified as a fruit. While it is commonly treated as a vegetable in culinary contexts due to its savory flavor profile, it meets the criteria for fruit defined by botanical standards.
In botanical terms, a fruit is the ripened ovary of a flower, which typically contains seeds. The eggplant is the fruit of the Solanum melongena plant, which belongs to the nightshade family, alongside tomatoes and potatoes. This classification is primarily based on its development from the flower and its seed-bearing capabilities.
Nutritional Benefits of Eggplant
Eggplants are not only versatile in cooking but also packed with a variety of beneficial nutrients. They contain key vitamins and minerals which contribute to overall health.
See also:
- Rich in Fiber: Eggplants are a good source of dietary fiber, which aids in digestion.
- Low in Calories: They are low in calories, making them a great addition to weight management diets.
- Antioxidants: Eggplants contain antioxidants, like nasunin, which help protect cells from damage.
Culinary Uses of Eggplant
In culinary terms, eggplants are exceptionally versatile, appearing in dishes across various cuisines around the world. Their texture and ability to absorb flavors make them a favored ingredient.
- Grilled or Roasted: Eggplants can be sliced and grilled or roasted to enhance their flavor.
- In Curries: They are often included in curries, where they absorb the spices and sauces.
- Pasta Dishes: Eggplants make a hearty addition to pasta sauces and baked dishes like lasagna.
Growing Eggplants
Growing eggplants can be a rewarding experience, as they thrive in warm conditions and require specific care. Understanding their growth cycle and habitat is crucial for successful cultivation.
- Sunlight Requirements: Eggplants need full sunlight, ideally 6-8 hours a day.
- Soil Needs: They prefer well-drained, fertile soil rich in organic matter.
- Watering: Consistent watering is essential, particularly during dry spells.
Common Varieties of Eggplant
There are numerous varieties of eggplant, each with unique features and flavors, catering to different culinary applications. Here are a few popular types:
- American Purple: Characterized by its deep purple color, it is one of the most common varieties.
- White Egg: A smaller, rounder variety that is milder in flavor.
- Thai Eggplant: Often green and small, these eggplants are commonly used in Southeast Asian dishes.
Health Considerations
While eggplants are generally beneficial, there are certain health considerations to keep in mind, especially for specific individuals.
- Nightshade Sensitivity: Some people may be sensitive to nightshades, which could lead to discomfort.
- Oxalates: Eggplants contain oxalates, which can be an issue for individuals with kidney stones.
- Fiber Intake: Overconsumption of eggplant may lead to digestive issues for some, particularly high fiber levels.
What is the 52 million year old fruit?

The 52-million-year-old fruit is the fossilized remains of a type of fig known scientifically as Ficus. This ancient fruit has been discovered in the Layers of sediment in the Green River Formation, located in present-day Wyoming, USA. The fossil records suggest that figs have existed for a remarkably long period, indicating their evolutionary history and ecological importance.
Fossil Discovery
The discovery of the fossilized fig occurred in the early 20th century, revealing a wealth of information about the floral diversity during the Eocene Epoch. These fossils were found embedded within sedimentary rock layers, which provided the right conditions for preservation.
- Fossils are formed through mineral replacement and compression of organic material over time.
- The geological formations indicate that this area was once a tropical environment.
- These discoveries help scientists understand the climate conditions of ancient Earth.
Significance of Figs
Figs, particularly the species related to the 52-million-year-old fossil, play a pivotal role in ecosystems around the world. They are not only important for their nutritional value but also for their ecological relationships.
- Figs are a food source for various wildlife, including birds and mammals.
- They are known for their unique pollination process that involves specific wasp species.
- Figs contribute to overall biodiversity by providing habitats for numerous organisms.
Comparative Age of Figs
The age of the fossilized fig provides context for the evolutionary lineage of plants. While modern figs have evolved, the ancient remains indicate that certain characteristics have remained relatively unchanged.
- Fossil evidence suggests that many plant species have existed for millions of years.
- Comparative studies reveal both similarities and differences in plant evolution.
- These connections to modern species help researchers track the timeline of plant adaptation.
Impact on Modern Botany
Fossilized fruits like the ancient fig have influenced botanical research and studies. They provide critical insights into how current plants adapted to climate changes over millions of years.
- Fossil findings can guide modern conservation efforts for fig species.
- They shed light on the relationships between past and present flora.
- Through studying these fossils, botanists can better understand plant response to environmental shifts.
Research and Methods
Scientists utilize various paleobotanical techniques to study fossilized fruits, including microscopy and isotopic analysis. Through these methods, they can infer details about the ecology of the period in which the figs thrived.
See also:
- Extracting DNA from ancient plant fossils provides insights into genetic diversity.
- Understanding the chemical composition helps reconstruct past climates.
- These methods enable scientists to visualize how plants interact with their environment over time.
What is the oldest fruit in America?

The oldest fruit in America is often considered to be the papaya. Native to the tropical regions of the Americas, particularly in southern Mexico and northern Central America, the papaya has been cultivated for thousands of years. Archaeological evidence suggests that papayas were being grown by indigenous peoples long before the arrival of Europeans in the 16th century. This fruit not only provided sustenance but also played a vital role in the culture and agriculture of pre-Columbian societies.
Historical Significance of Papaya
The papaya holds a special place in the agricultural history of the Americas. It was introduced to the world by indigenous communities who recognized its nutritional value and versatility. The fruit was used for various culinary purposes and was also valued for its medicinal properties.
- Indigenous Cultivation: Evidence shows that indigenous people cultivated papayas as early as 500 A.D.
- Cultural Practices: Papayas were often integrated into rituals and celebrations due to their significance.
- Trade Routes: The cultivation of papayas influenced trade among different indigenous cultures.
Nutritional Benefits of Papaya
Papaya is not only one of the oldest fruits but also one of the most nutritious. It is rich in vitamins, enzymes, and antioxidants that contribute to various health benefits.
- Vitamin Content: Papayas are high in vitamin C, vitamin A, and folate.
- Digestive Health: The enzyme papain aids digestion, making it beneficial for gut health.
- Antioxidant Properties: Papayas contain antioxidants that help combat oxidative stress in the body.
The Role of Papaya in Modern Cuisine
In contemporary culinary practices, papaya remains a beloved ingredient across various cuisines. Its sweetness and unique flavor enhance dishes, making it a versatile choice for chefs and home cooks alike.
- Fresh Salads: Papaya is often used in fruit salads for its sweetness and texture.
- Cooking: It can be grilled or cooked in savory dishes for added flavor.
- Desserts: Papaya is a popular ingredient in smoothies and desserts due to its natural sweetness.
Global Spread of Papaya
Following its domestication in the Americas, papaya was exported to various parts of the world, particularly after European explorers took the fruit back to Europe in the 16th century. This led to its widespread cultivation worldwide.
- Introduction to Asia: The fruit was introduced to Asia, becoming widely cultivated in countries like India and the Philippines.
- Adaptation: Papaya adapted well to tropical and subtropical climates, expanding its cultivation range.
- Cultural Integration: Different cultures incorporated papaya into their cuisines and practices.
Environmental Considerations
The cultivation of papaya in contemporary times also raises important environmental considerations. Sustainable practices are essential to ensure that papaya farming does not harm the ecosystems where it is grown.
- Sustainable Farming: Emphasizing organic farming practices can reduce chemical use.
- Biodiversity: Maintaining genetic diversity is critical for the adaptability of papaya in changing climates.
- Soil Health: Practices that promote soil health are essential for the long-term productivity of papaya crops.
Questions from Our Readers
What is the oldest fruit to exist?
The oldest known fruit is the fig. Fossil evidence suggests that the fig tree existed as far back as 11,400 years ago, making it one of the earliest domesticated fruits.
What characteristics make the fig special?
Figs are unique due to their high nutritional value and the fact that they grow in a variety of climates. They are rich in fiber, vitamins, and antioxidants, making them a healthy choice for fruit lovers.
How did figs influence ancient cultures?
Figs played a significant role in various ancient civilizations, often representing fertility and prosperity. They were cultivated in regions like the Mediterranean, where they were a staple food and used in religious rituals.
Are there any other ancient fruits?
Yes, besides figs, other ancient fruits include the pomegranate and the date, both of which have been cultivated for thousands of years. These fruits not only contributed to the diet but also held cultural significance in the societies that grew them.
See also:

If you want to read more articles like Discovering What is the Oldest Fruit to Exist? A Journey Through Time, we recommend you check out our Plants category.
Leave a Reply
Related Articles