Which Plants Do Not Like Egg Shells? Discover the Best Choices for Your Garden!

When it comes to garden care, utilizing natural amendments can be beneficial, yet not all plants thrive with the same materials. Eggshells, often praised for their calcium content, can enhance soil health for many plants; however, some species may not appreciate this addition. Understanding which plants do not like eggshells is crucial for optimizing your garden's environment. In this article, we will explore the best choices for your garden and highlight those plants that might be adversely affected by eggshells, ensuring you make informed decisions for a thriving green space.
Which Plants Are Adversely Affected by Egg Shells?
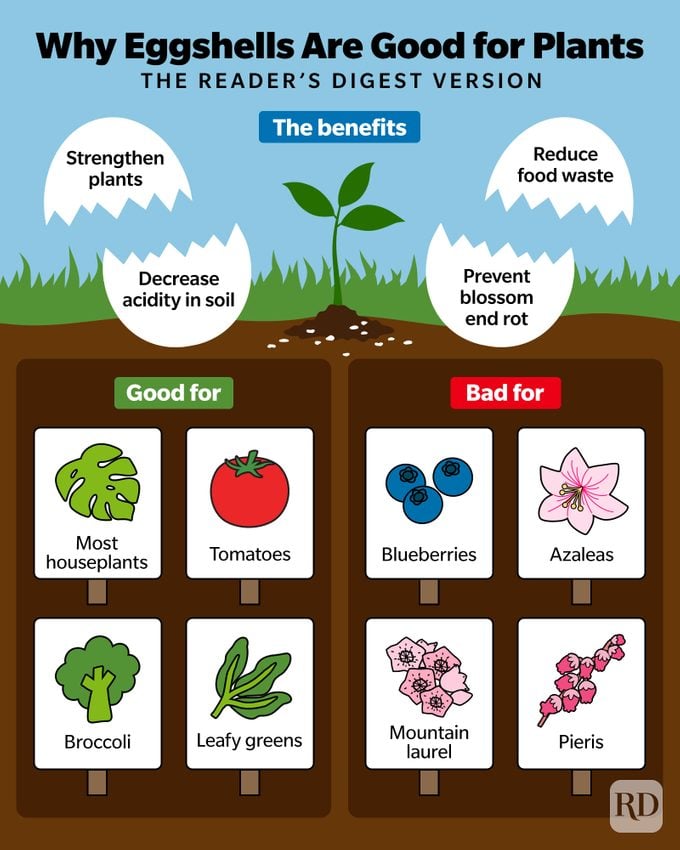
Certain plants may not thrive when eggshells are added to their soil. The calcium provided by eggshells is beneficial to many plants; however, some species can be sensitive to the increased alkalinity that shells can introduce into the soil. For instance, plants that prefer acidic conditions, such as blueberries, azaleas, and rhododendrons, may struggle if the pH of their growing medium rises due to the presence of eggshells. Moreover, certain fungi and pests that flourish in alkaline environments can become problematic for these plants, potentially leading to reduced health or growth issues.
Blueberries
Blueberries are highly sensitive to soil pH and thrive in acidic conditions, ideally between 4.5 and 5.5. When eggshells are added to the soil, they can raise the pH level, making it less suitable for these plants. This change can inhibit nutrient absorption, particularly affecting iron uptake, which is crucial for blueberry health and fruit production.
Azaleas
Azaleas, like blueberries, prefer acidic soil, and the addition of eggshells can alter the pH balance unfavorably. High pH can lead to deficiencies in essential micronutrients, which may manifest as yellowing leaves or poor flowering. Maintaining the correct soil environment is crucial for the well-being of these vibrant shrubs.
Rhododendrons
Rhododendrons have specific soil requirements that favor acidity; thus, incorporating eggshells can disrupt their ideal conditions. An increase in soil alkalinity due to eggshells can detrimentally impact their nutrient uptake, leading to weak growth and diminished flowering potential.
Plants With High Iron Requirements
Plants that require high levels of iron, such as certain ornamental grasses and flowering plants, can be adversely affected by the addition of eggshells. The rise in soil pH can lead to iron chlorosis, a condition where plants exhibit yellowing of leaves due to insufficient iron, impeding their growth and vitality.
Vegetables Like Tomatoes and Peppers
While some gardeners use eggshells to deter pests, certain vegetable plants like tomatoes and peppers can also react negatively to changes in soil pH. Increased alkalinity can lead to nutrient imbalances, ultimately affecting fruit quality and plant health. It's essential for these vegetables to maintain a balanced soil environment for optimum growth.
| Plant | Preferred pH | Effect of Eggshells |
|---|---|---|
| Blueberries | 4.5 - 5.5 | Increased pH leading to nutrient deficiencies |
| Azaleas | 5.0 - 6.0 | Alkalinity disrupts micronutrient absorption |
| Rhododendrons | 5.0 - 6.0 | Higher pH causes weak growth |
| Iron-requiring plants | Varies | Susceptible to iron chlorosis |
| Tomatoes | 6.0 - 6.8 | Poor fruit quality due to pH imbalance |
Are there any plants that don't like egg shells?
There are indeed some plants that may not appreciate the addition of egg shells to their soil. While egg shells are generally a good source of calcium and can help improve soil structure, certain plants can be sensitive to the conditions created by the presence of egg shells. Here are several aspects to consider regarding plants that might not thrive with egg shells.
Plants Sensitive to Calcium
Certain plants prefer lower levels of calcium in their soil. Excess calcium can lead to nutrient imbalances that adversely affect plant growth. Examples of such plants include:
See also:
- Blueberries - These thrive in acidic soils and may suffer from nutrient lockout if the pH is raised too high from calcium-rich amendments.
- Rhododendrons - Similar to blueberries, rhododendrons prefer acidic conditions and may not perform well with added calcium.
- Azaleas - They also favor acidic soils and can be negatively impacted by the alkaline effects of egg shells.
Soil pH Considerations
Adding egg shells can alter the pH level of the soil, making it more alkaline. Many plants are sensitive to pH changes, especially those that thrive in specific pH ranges. For instance:
- Fern Species - Many ferns prefer more acidic environments and can become stressed with increased alkalinity.
- Amaryllis - This plant prefers well-drained, slightly acidic soil and might be negatively affected by the alkaline nature of ground egg shells.
- Gardenias - These are particularly sensitive to soil pH; an increase in alkalinity due to egg shells can lead to nutrient deficiencies.
Nutrient Competition
Egg shells can affect nutrient availability in the soil by providing calcium but potentially causing an imbalance with other essential nutrients. This particularly impacts:
- Tomatoes - While they do benefit from calcium, too much can lead to magnesium deficiencies.
- Peppers - Like tomatoes, they need a balanced nutrient regimen, and excessive calcium can disrupt this balance.
- Potatoes - An excess of calcium can lead to deficiencies in potassium, essential for tuber formation.
Potential Pests and Diseases
Alterations in the soil environment from adding egg shells can sometimes attract pests or promote diseases, which can be detrimental to certain plants:
- Leafy Greens - Excess calcium can lead to a decrease in moisture retention in the soil, which may attract pests like aphids.
- Brassicas - These might be more prone to root rot if the soil remains dry due to poor moisture retention after adding egg shells.
- Herbs - Certain herbs may attract pests when nutrients are out of balance.
Environmental Aspects
The general environment of the plant— including its growing conditions—will determine how it reacts to egg shells. Some environmental factors to consider are:
- Watering Practices - Consistent soil moisture is crucial; any imbalance caused by egg shells can affect this.
- Sunlight Exposure - Plants in full sun may have different nutrient needs compared to those in shaded areas, influencing how they react to added calcium.
- Soil Texture - Heavier soils may retain water differently than lighter soils, affecting how egg shells influence moisture and nutrient uptake.
Are egg shells bad for any plants?
Eggshells are a popular natural amendment in gardening due to their high calcium content. While they are generally beneficial for most plants, there are nuances regarding their impact on certain species. Here, we explore if eggshells can be bad for any plants and provide related insights.
Understanding the Nutritional Benefits of Eggshells
Eggshells are primarily composed of calcium carbonate, which is essential for plant health. When broken down, they can provide a slow-releasing source of calcium for plants. This is especially beneficial for:
- Tomatoes - To prevent blossom-end rot.
- Peppers - To support healthy growth.
- Cabbage and related plants - To aid in stronger cell walls.
Potential Drawbacks of Eggshells in Gardening
Although beneficial, some plants may not respond well to the addition of eggshells. This can depend on soil pH and particular plant species. Some potential drawbacks include:
- High pH Sensitivity - Certain plants require acidic soil and may suffer in alkaline conditions.
- Mineral Imbalance - Overuse can disturb soil mineral ratios.
- Pest Attraction - Deteriorating shells can attract pests.
Specific Plant Types That May Be Affected
Certain plants have shown sensitivity to added calcium from eggshells. The following are examples:
- Blueberries - Prefer acidic conditions and may struggle with an increase in soil pH.
- Azaleas - Can show signs of nutrient deficiencies in alkaline soils.
- Rhododendrons - Similar pH preferences as azaleas.
How to Properly Use Eggshells in Your Garden
To maximize benefits and minimize potential issues, it's essential to apply eggshells correctly. Consider these tips:
See also:
- Crush Thoroughly - Smaller pieces break down more quickly, enhancing calcium availability.
- Compost First - Composting can balance nutrient content before adding to soil.
- Monitor pH Levels - Test soil regularly to ensure it remains within the optimal range for your plants.
Alternative Uses for Eggshells
If eggshells are not suitable for certain plants, there are alternative uses that retain their benefits without direct soil application:
- Natural Pest Deterrent - Sprinkle crushed shells around plants to deter soft-bodied pests.
- Seed Starter Pots - Use halves as biodegradable seed starters.
- Calcium Source for Chickens - Feed crushed shells back to chickens for improved egg production.
What plants should I put egg shells around?
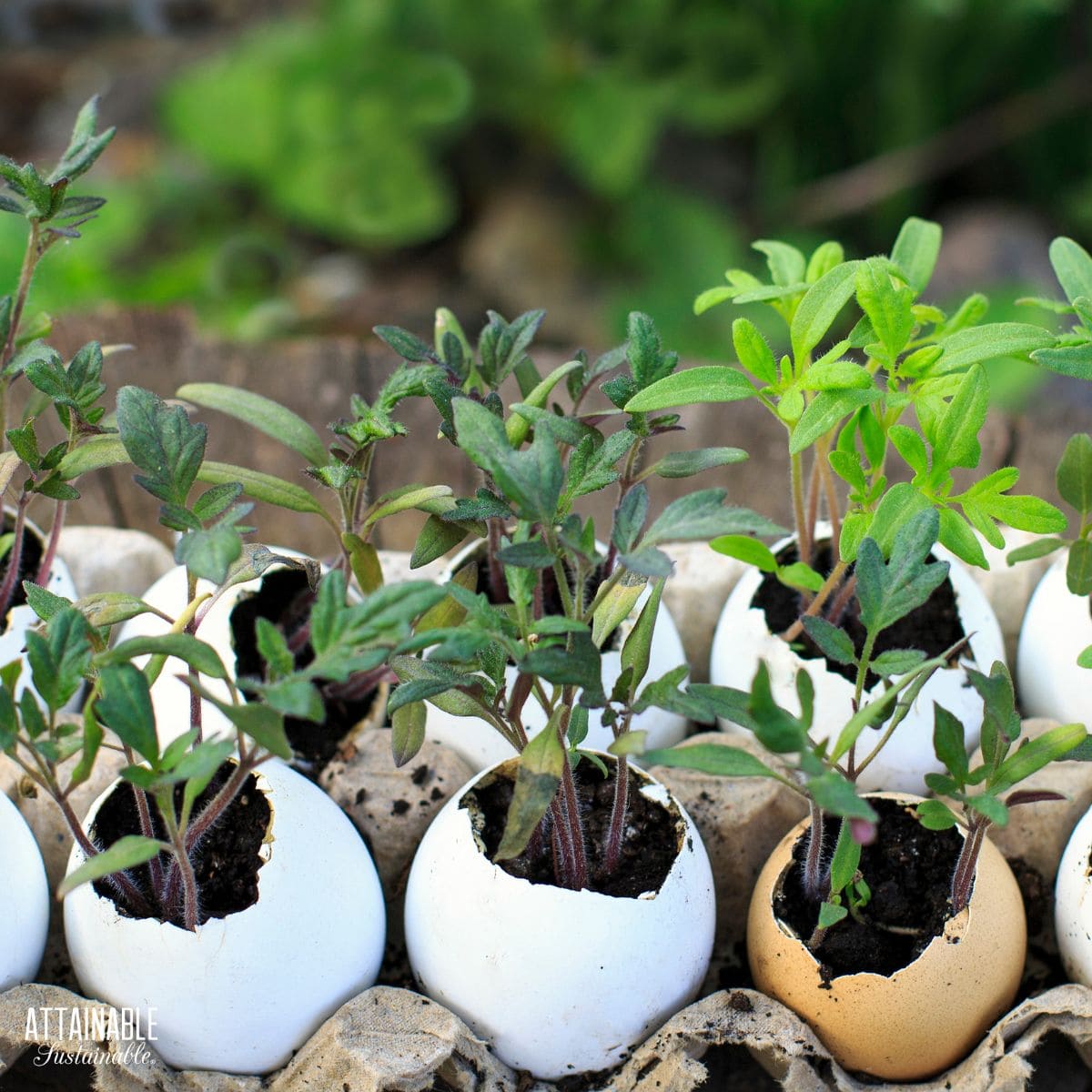

Eggshells are a great addition to the garden as they provide a sustainable source of calcium and can help deter certain pests. When considering which plants to place eggshells around, it's important to choose those that benefit most from the nutrients and protection that these shells provide.
Benefits of Eggshells in the Garden
Eggshells are composed primarily of calcium carbonate, a crucial nutrient for many plants. Here are some benefits:
- Calcium Supply: Helps strengthen cell walls in plants.
- Pest Deterrent: The sharp edges of crushed eggshells can deter snails and slugs.
- Soil Amendment: Improves soil structure over time as they break down.
Plants That Benefit from Eggshells
Certain plants thrive when eggshells are used as a mulch or soil amendment. Here are some of the best candidates:
- Tomatoes: They require calcium to prevent blossom end rot.
- Peppers: Encourage overall growth and fruit quality with calcium-rich soil.
- Eggplants: Similar to tomatoes, they benefit from extra calcium for robust growth.
How to Prepare Eggshells for Use
Proper preparation of eggshells enhances their effectiveness. Here’s what you should do:
- Wash: Rinse eggshells to remove any remaining egg residue.
- Dry: Allow them to dry completely to prevent molding.
- Crush: Use a rolling pin or mortar and pestle to crush them into smaller pieces.
How to Apply Eggshells Around Plants
Applying crushed eggshells around plants requires some care to maximize benefits:
- Layering: Spread crushed eggshells around the base of the plant.
- Mixing: Incorporate them into the soil when planting to improve nutrient content.
- Reapplication: Add more eggshells periodically to maintain soil calcium levels.
Other Uses for Eggshells in the Garden
Beyond being placed around specific plants, eggshells have various uses in the garden:
- Composting: Add crushed eggshells to your compost pile for an extra calcium boost.
- Seed Starters: Use halved shells as biodegradable seedling pots.
- Plant Food: Blend into powder to create homemade plant food rich in calcium.
Questions from Our Readers
Which plants do not benefit from eggshells?
Eggshells are beneficial for many plants, but some, like acid-loving plants such as blueberries, raspberries, and azaleas, might not benefit from them. This is because eggshells can raise the pH level of the soil, making it less acidic, which these plants prefer.
Can eggshells harm any specific types of plants?
Yes, applying eggshells can potentially harm plants that thrive in low pH environments, such as ferns and certain ornamental plants. Excess calcium carbonate from eggshells can lead to nutrient imbalances in the soil, affecting the plants' growth.
See also:
Is there a risk of pests when using eggshells around plants?
While eggshells can deter some pests, their effectiveness varies. In some cases, they might attract snails and slugs, which enjoy the decaying organic matter. It's important to monitor your garden's pest levels if utilizing eggshells as a protective barrier.
How should I prepare eggshells before using them in my garden?
To maximize their benefits, you should clean and dry the eggshells thoroughly. After drying, crush them into small pieces or grind them into a fine powder. This makes it easier for plants to absorb the nutrients found in the shells, ensuring they offer the best results.

If you want to read more articles like Which Plants Do Not Like Egg Shells? Discover the Best Choices for Your Garden!, we recommend you check out our Plants category.
Leave a Reply

Related Articles